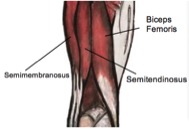
Let’s get clued up on hamstring strains; why you may have one, what you can do to help and how to prevent a future injury. The hamstrings are a group of three muscles; the biceps femoris, semimembranosus and semitendinosus. You can feel these muscles if you place your hands on your sitting bones where the muscles originate and slide your hands down the back of your legs. The main action of these muscles is to bend your knee, take your leg out behind you and to assist rotation of your knee, especially when performing accelerating and decelerating actions.
A strain/pull/tear is when the muscle fibres are overstretched. Injuries are frequently felt as a short sharp pain in the back of your thigh whilst exercising. A hamstring strain will typically happen when running just before your foot hits the ground. At this point, the hamstrings are working eccentrically to control the forward motion of the two lower leg bones, your tibia and fibula. Pain is often the most debilitating symptom affecting your ability to continue exercising and may cause a limp. Other symptoms include swelling, bruising, muscle spasm and reduced movement at your knee.
Strains can be categorised into 3 different grades. 1 being the mildest with a small number of fibres being torn to grade 3 being the most severe which can be a complete muscle rupture. The good news is muscles have a fantastic blood supply and should heal within 3-12 weeks depending on the degree of injury. However, the flexible skeletal muscle fibres, which your muscles are made up of, are replaced with much more inflexible tough scar tissue, which is where physio’s come in. Specific rehabilitation such as specialist stretching, strengthening, taping and soft tissue techniques can dramatically influence how muscle fibres are restructured reducing the amount of scar tissue speeding up the healing process helping you return to sport quicker. With any soft tissue injury, R.I.C.E (rest, ice, compression, elevation) should always be your first response.
A physio will be able to perform a thorough assessment and educate you on why you sustained a hamstring strain in the first place. Common factors that can predispose you to hamstring strains are not warming up or cooling down properly, tight hamstrings or hip flexors, weak hamstrings or gluteal (butt) muscles, training at a high intensity without adequate training or altered biomechanics.
Runners often have short, weak hamstrings, tight hamstrings will restrict the length of your strides when running meaning you have to work harder to cover the same distance as you would with adequately lengthened hamstrings. Chronically tight hamstrings can cause not only hamstring strains but can contribute to back pain, knee pain and leg length discrepancies. So even if you have never stretched before it may be a good time to start stretching!
So to prevent yourself pulling a hammy make sure you warm up and cool down properly including effective stretching of not just your hamstrings but hip flexors, quadriceps and calf muscles, do sport specific strength and conditioning and avoid sudden increases in intensity of exercise. On your next visit why not ask your physio and find out how healthy your hamstrings are