What is frozen shoulder?
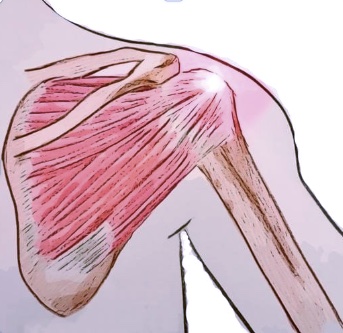
Frozen Shoulder (also known as Adhesive Capsulitis) is a condition that affects the shoulder joint with no apparent (idiopathic) cause. It is characterised by severe pain and stiffness of the shoulder. The shoulder capsule thickens due to lack of synovial fluid, which leads to tightness and stiffness. Frozen shoulder occurs most frequently between the ages of 40-60 years old and affects more women than men.
How does it happen?
The cause of Frozen Shoulder is still unknown, however some risk factors have been identified that increase your chances of developing the condition including diabetes mellitus, stroke, shoulder injuries and immobilisation.
The hallmark sign of Frozen Shoulder is being unable to move your shoulder even with the help of other people. This is particularly noticeable when moving the arm away from the body. Physicians may ask you to undergo investigations such as X-ray and MRI, however frozen shoulder doesn’t tend to show up on imaging.
What are the symptoms?
Frozen Shoulder has three stages:
1. Freezing (Painful stage) – lasts from six weeks to nine months; patient has a slow onset of pain (usually pain at rest), and the shoulder starts to experience limitation of motion
2. Frozen (Adhesive stage) – lasts from four to six months; pain begins to diminish (the shoulder is still usually painful with movement), of the shoulder getting stiffer, and activities of daily living are affected).
3. Thawing (Recovery stage) – last six months to two years; shoulder’s normal range of motion is slowly returning to normal
How can physiotherapy help?
Though Frozen Shoulder is a self-limiting condition, an important part of physiotherapy management is the prevention of related neck and shoulder issues secondary to the original problem. As you can imagine, frozen shoulder can be extremely debilitating and many adaptations occur in the surrounding musculature. Physiotherapy also acts to reduce pain throughout phases one and two, while restoring joint movement as the joint moves through the painful phase. This is done through a variety of treatments, including heat, stretching, joint mobilisation, range of motion exercises to improve shoulder’s motion and resistance exercise to strengthen, you will also be given a home exercise program. Recovery time varies with every patient. If you’re working hard to regain your normal shoulder function, you’ll be rewarded with a faster recovery.
Medical management includes medications and corticosteroids, joint manipulation while under anaesthetic and/or surgery, however at this point nothing has come close to providing a consistent and simple cure.
None of the information in this article is a replacement for proper medical advice. Always see a medical professional for advice on your individual condition.