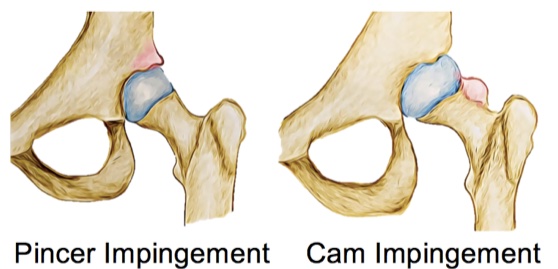
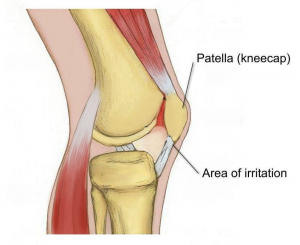
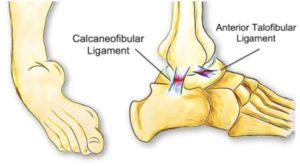
CUMBERLAND PHYSIOTHERAPY PARRAMATTA: Most tissues in the body have healed completely in six to 12 weeks following an injury, however, many people have severe pain that lasts much longer than this. We know that the intensity of the pain you feel is not always associated with a similar amount of damage. In some cases, there can be a severe amount of pain with almost no detectable damage. With this in mind, we explore some reasons why your pain might not be getting better, long after the tissues have healed.
You’re afraid of the pain.
Pain can mean many different things, for some of us pain can affect our ability to work or can be a symptom of a serious disease. What you believe about your pain can either amplify or reduce the symptoms you experience. If you feel that every time you experience pain you are causing more damage, you will naturally pay more attention to this and your nervous system will amplify the signals in an attempt to keep you safe.
If you understand the cause of your pain and know that while there is discomfort, you are not in danger of causing more damage, often the pain will feel less severe. This is one of the benefits of seeing a physiotherapist after your injury as they can help you to understand your pain, giving you more control over your recovery.
You started moving differently after the injury.
Immediately after an injury, it’s natural to change the way you move to avoid painful movements. After a while, these changed movement patterns can become maladaptive and actually begin to cause pain and discomfort on their own due to the altered stress patterns placed on your body.
Correcting these adaptive movement patterns can often go a long way in reducing pain after an injury. You might not have noticed these changes and might need a physiotherapist to identify and help you to return to your usual movement pattern.
You have lost muscle strength since the injury.
While a certain amount of rest following an injury is always helpful, if we stop moving altogether, our muscles can lose strength. This can mean that our posture changes, we fatigue easier during our usual activities and that we are more susceptible to further injury. Less movement also means we actually focus on the pain more when it does happen. Physiotherapists are able to advise you on the right types and amounts of excercise for you in the period following your injury.
The pain has affected your lifestyle.
When pain affects your ability to sleep, work and even concentrate, it’s not surprising that this can have a negative affect on your overall wellbeing and mental health. This can create a negative cycle of anxitey and depression that perpetuates and increases the experience of pain. If your pain is really getting you down, speaking to a mental health professional can actually be a valuable part of your physical recovery.