CUMBERLAND PHYSIOTHERAPY PARRAMATTA:
A “pain in the butt” is often used as a funny expression, but when it happens in real life, it can be anything but amusing. Whether it’s a dull ache or a sharp jab, pain in the buttocks can make sitting, walking, or even sleeping a challenge. There are a variety of possible causes, and an accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Here’s a breakdown of five of the most common causes of buttock pain.
1. Piriformis Syndrome
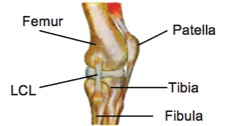
This condition occurs when the piriformis muscle—located deep in your buttock—irritates the sciatic nerve that runs beneath it. This can lead to pain, tingling, or numbness in the buttock and sometimes down the back of the leg. It’s often mistaken for sciatica but isn’t caused by a spinal issue. Overuse, prolonged sitting, or direct trauma to the buttock can all trigger piriformis syndrome.
2. Sciatica
Sciatica refers to pain caused by irritation of the sciatic nerve, typically due to a herniated disc or spinal stenosis in the lower back. While the source is in the spine, the pain often radiates through the buttock and down the leg. It’s usually felt on one side and can be sharp, shooting, or burning. Sitting for long periods often makes it worse.
3. Sacroiliac (SI) Joint Dysfunction
The sacroiliac joints connect your pelvis to the base of your spine. When they become inflamed or move abnormally—due to pregnancy, arthritis, or trauma—they can cause deep pain on one or both sides of the buttock. SI joint pain often worsens with activities like standing up from a seated position, climbing stairs, or even rolling over in bed.
4. Gluteal Muscle Strain
Just like any other muscle, the glutes can be overstretched or injured—especially during exercise, heavy lifting, or sudden movement. A strain or tear in the gluteal muscles causes localized buttock pain that tends to worsen with movement, especially walking uphill or climbing stairs. It may also feel sore to touch.
5. Ischial Bursitis
Also known as “Weaver’s Bottom, ” ischial bursitis occurs when the small fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion the bones in your bottom become inflamed. It’s commonly caused by prolonged sitting on hard surfaces or repetitive motion like cycling. This condition leads to a dull ache or sharp pain at the base of the buttock, especially when sitting.
What to do if you have persistent buttock pain?
In most cases, the first step in resolving pain is getting an accurate diagnosis. Many different conditions can refer pain to the buttock, so it’s essential to seek a professional opinion. Your physiotherapist can rule out any serious causes and help identify contributing factors. None of the information in this article is a replacement for proper medical advice. Always see a medical professional for advice on your individual injury.